Special Relativity: Connecting to General Relativity
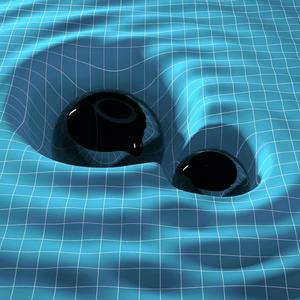
In this final episode, Jennifer and Inara explore how Einstein’s Theory of Special Relativity revolutionized physics, paving the way for General Relativity and a new understanding of gravity, time, and space.Special Relativity dismantled Newton’s absolute universe, showing that space and time are not separate but interwoven into a single entity—spacetime. It introduced time dilation, length contraction, and simultaneity, revealing that time flows differently for observers in motion. Yet, special relativity only worked in flat spacetime—it couldn’t explain gravity or acceleration.This limitation led Einstein to his greatest insight: General Relativity. Instead of Newton’s view of gravity as a force, Einstein proposed that mass and energy curve spacetime itself, guiding objects along natural paths. This theory predicted gravitational time dilation, light bending around massive objects, and even black holes. The famous 1919 solar eclipse experiment, led by Arthur Eddington, confirmed Einstein’s predictions, catapulting him to global fame.Relativity’s predictions continue to be tested today. The LIGO observatory’s 2015 discovery of gravitational waves, ripples in spacetime from colliding black holes, was a triumph for Einstein’s theory. In 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope captured the first-ever image of a black hole’s event horizon—another stunning confirmation.But challenges remain. General Relativity and Quantum Mechanics remain incompatible, creating a fundamental gap in physics. The search for a unified "Theory of Everything", through approaches like String Theory and Loop Quantum Gravity, continues.Einstein’s legacy extends far beyond physics—his ideas shaped technology, philosophy, and our very understanding of reality. Over a century later, his vision continues to inspire scientists, philosophers, and dreamers alike.-------------------------Listen to all the episodes on The Turing App https://theturingapp.com/show_index/theory-of-relativityWhat if time isn’t absolute? What if moving objects shrink and clocks tick slower at high speeds? Join us on a journey through Einstein’s mind-bending theory of special relativity—without the math. Discover why the speed of light is constant, how time dilation and length contraction reshape reality, and what E = mc² truly means. With vivid stories like the twin paradox, train-lightning thought experiments, and pole-and-barn debates, this series breaks down the science that redefined time and space. Whether you're curious or just love a good brain teaser, explore how Einstein’s ideas changed everything we thought we knew.Explore science like never before—accessible, thrilling, and packed with awe-inspiring moments. Join us on an adventure to fuel your curiosity with 100s of curated audio showshttps://theturingapp.com/#GeneralRelativity #SpecialRelativity #EinsteinTheory #SpacetimeCurvature #RelativityExplained #TimeDilation #GravitationalWaves #BlackHolePhysics #QuantumConnections #MillenniumPhysics #CosmicExpansion #PhysicsForEveryone #UnderstandingRelativity #ClayInstitute #MathematicalPhysics #EventHorizon #GravitationalLensing #PhysicsPodcast #TheoryOfEverything #AstrophysicsSimplified #EinsteinLegacy #RelativityRevolution #TheTuringApp #RelativitySeries #EinsteinThoughtExperiments